Of the four key components of a computer which are Input, Output, Storage, and Processor, only the peripheral devices are visible and accessible directly. The CPU processor, internal memory, network cards are all hidden. Kind of like in a car where we only see and access the “pretty” parts like the wheel, car seats, dashboard, etc. The engine, battery, all the wires and cabling is hidden under its hood or bonnet. Let’s see what’s “under the hood” of a computer.
Where, in the picture to the right, is the CPU?
If you guessed it’s in the rectangular box that’s sitting right next to the monitor, you are right! While the whole setup with the mouse, keyboard, monitor and the tower is generally termed as a computer, the main processing components like the motherboard and the CPU are safely encased within the walls of that “tower”.
In a laptop, there is no “tower”. The components are very compact and encased under the keyboard making your laptop portable.
There are several components under the hood of a computer tower or laptop. Some of the main ones are:
- Motherboard
- RAM slots
- Hard drive
- CPU
- Heat sink
- Expansion slots
- Connectors
- PSU (Power Supply Unit) – Battery
Let’s look at this video that gives a tour of these components inside a laptop.https://www.youtube.com/embed/EVl0bkMC9uw?feature=oembed
Here’s another really good video on the inner components of a computer.
Let’s look at each of these components –
Motherboard – This is where all the action is to make a computer work. It is a flat printed circuit board (PCB) that has all the key, sensitive electronic components mounted on it.
Previously wires connecting all the components made it very hard and bulky to manage the complex and massive circuitry. But with a PCB, the connections are soldered on to the board removing the need for thousands of wires crisscrossing.
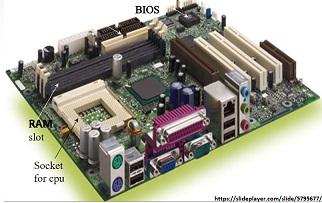
On the PCB are all the key components needed by the computer to perform its actions like the CPU, RAM slot with the RAM sticks, CMOS battery, BIOS chip, registers, expansion slots giving us a motherboard. It serves as a base to connect all the key electrical components to each other and to the external peripherals.
The first-ever Apple “computer” was just a flat board that did the computations. Users had to hook it up to a TV for display.
This is a motherboard fitted inside the tower of a desktop computer.
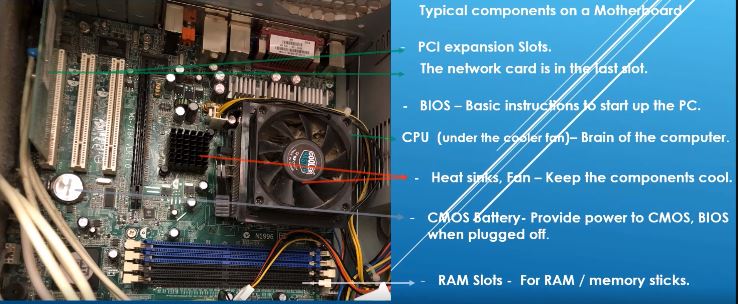
A closer look
CPU – Central Processing Unit. This is a small integrated chip mounted on the motherboard. The CPU is the “brain” of the computer and does the logic and processing. It is usually covered by a heat sink on the top to make sure the CPU remains cool and does not get over-heated. In the olden days the processing unit would be huge and all computers were in a “server” room that was kept very cold to offset the heat generated from them and keep them from over-heating.

Heat sink – A Heat sink helps keep the electrical components cool and takes the heat generated away from the electronic components on a motherboard. Additionally, there may be a cooling fan inside the tower or under a laptop to drive the heat away from the components.

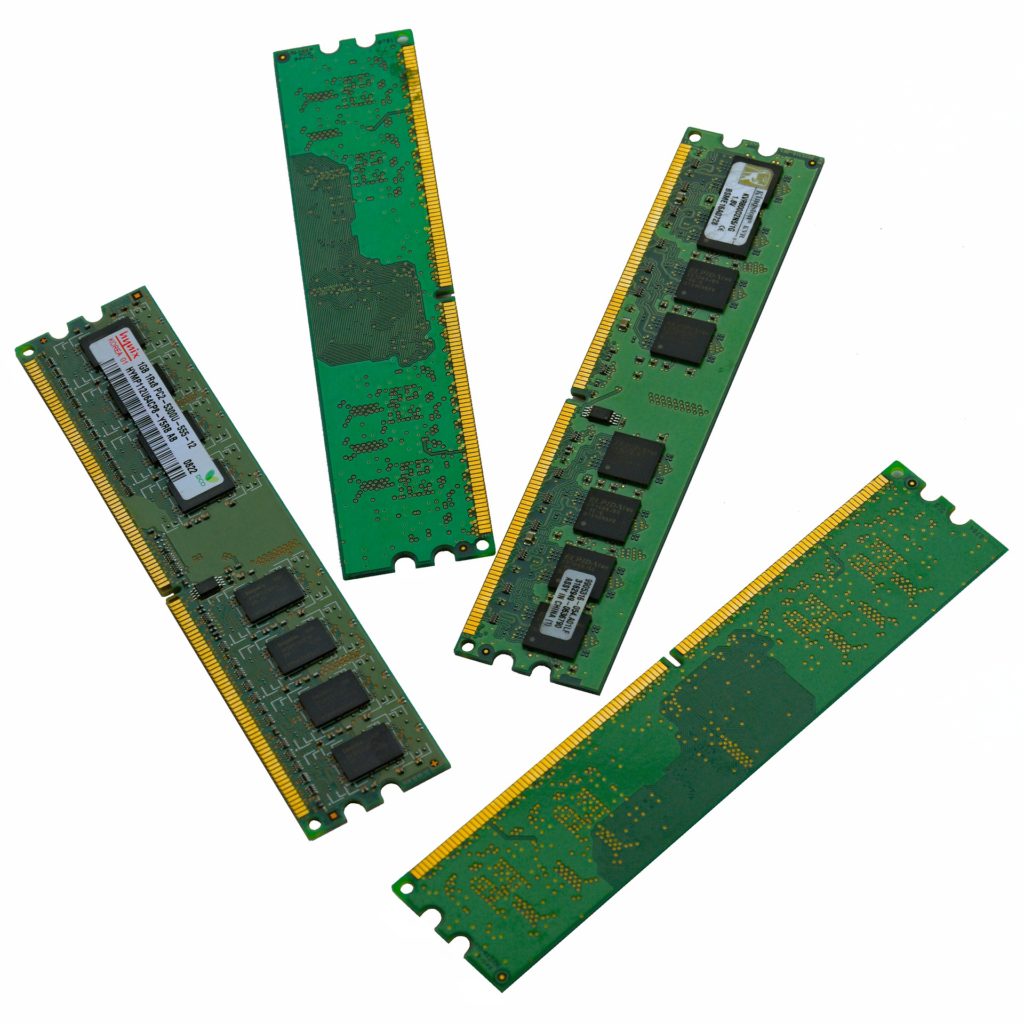
RAM and RAM slots – RAM stands for Random Access Memory. This is where the processor goes to get its working data quickly. RAM, also called as memory sticks are inserted into RAM slots on the motherboard (see the picture of the motherboard above). We will learn more RAM memory in our storage and memory topic. Memory sticks come in 8 MB or 16 MB capacities.
Expansion slots – These are slots just like the RAM slots on the motherboard but are meant for other accessories like a Network card and Graphics card that help add more functionality to your computer.
Connectors – These are the gateways to connect the outside, external components to the Motherboard. The connectors help to connect peripherals like the keyboard and the mouse to the motherboard and pass data in and receive output.


Hard drive – Internal hard drive is another important component of a computer, but is not mounted on a motherboard. It is a secondary storage that stores all the user data, files, applications. This is usually the “C drive” that you see when you save or retrieve files. Today, many light devices like the Chromebook do not have a user hard drive. So you cannot save files “locally” on the computer, Instead, they are stored in the cloud.
PSU (Power Supply Unit) – Battery – This is another important unit encased inside the tower or laptop and not visible to us unless we open up the case. A PSU is the source of power for the components to keep them running. We connect the power supply cable from the outside into the PSU’s end point connector to provide power to the computer. A laptop also comes with an internal battery that when charged, can provide power without being connected to a wired power source.

